

Under current MACRS depreciation rules, buildings are generally not subject to ordinary income recapture under Section 1245, because the depreciation is done on a straight-line basis. In this fact pattern, the LLC has a building that has appreciated by $400, of which $100 is D's share.

The third type of hot asset is ordinary income depreciation recapture. Inventory is also a "hot asset." Because D's share of the appreciation inherent in the inventory is $10, D must recharacterize another $10 of gain to ordinary income. For a full discussion of hot assets, see this previous Tax Geek Tuesday. Cash basis receivables are one of the three classes of "hot assets" under Section 751, and as a result, D must recharacterize $50 of his $160 gain as ordinary income. Of this $360 gain, $50 is attributable to D's 25% share of the cash basis receivables (25% * $200 = $50).
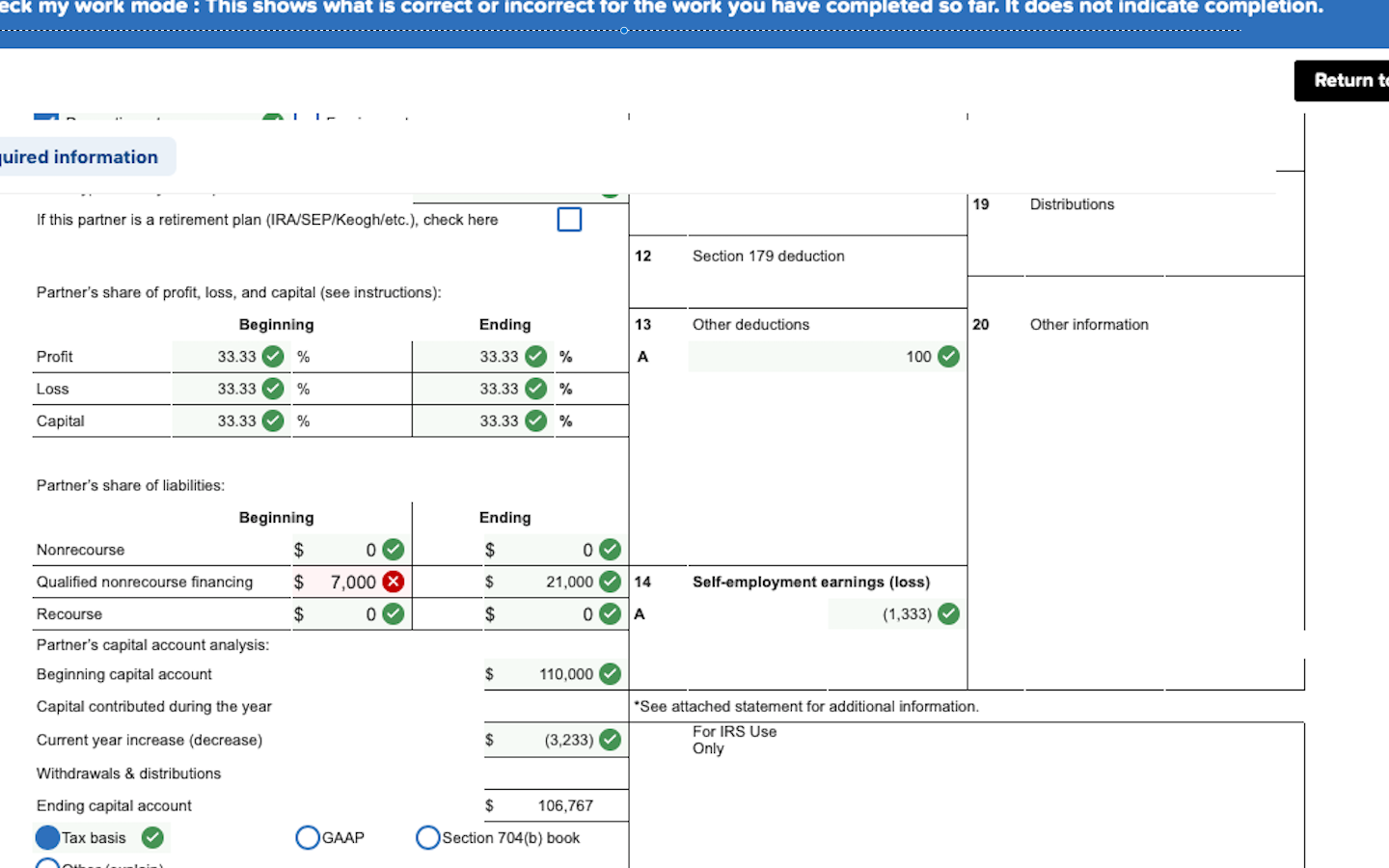
The sales price is $710 ($610 cash plus $100 of debt relief under Section 752), and D's tax basis is the interest is $350 ($250 capital account plus D's $100 share of partnership liabilities under Section 752). Under Section 1001, D will realize total gain on the sale of its interest to A, B and C of $360. How do the different transactions impact the tax consequences to D, to A, B, and C, and to LLC? In our hypothetical redemption scenario, LLC buys back D's interest for $610. In our hypothetical sale analysis, A B and C each buy 1/3 of D's interest for $203.33. While there are numerous non-tax considerations that must addressed in structuring the buyout, there are also subtle nuances under the tax law that will change the consequences to all involved depending on whether a "sale" or "redemption" is used. But who should purchase the interest, some or all of the other partners -A, B or C - in a "sale" transaction, or should the LLC simply buy back D's interest in a "redemption?" Due to D's penchant for spending his day viewing pornography on his work-issued smart phone, A, B and C all agree that D has to go, and that his interest should be purchased for its FMV of $610 (25% * $2,440).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
